Understanding the Basics of Urinary Retention
Before diving into the role of stress in causing and exacerbating urinary retention, it is important to first understand the basics of this condition. Urinary retention is a medical condition where an individual is unable to completely empty their bladder. This can be either acute, where it comes on suddenly and requires immediate medical attention, or chronic, where it persists over a longer period of time with less severe symptoms.
There are numerous factors that can contribute to urinary retention, such as nerve damage, an enlarged prostate, or certain medications. However, the relationship between stress and urinary retention is particularly noteworthy and worth exploring in greater detail.
Stress and Its Impact on the Body
Stress is a natural response to challenging situations that can have both beneficial and detrimental effects on the body. On one hand, stress can help us stay alert and focused, allowing us to perform better in certain situations. On the other hand, chronic stress can lead to a variety of health problems, including high blood pressure, weakened immune system, and mental health issues like anxiety and depression.
When it comes to the urinary system, stress can have a direct impact on bladder function and contribute to urinary retention. This is because stress can cause the muscles in the pelvic floor to tense up, making it more difficult for the bladder to empty completely.
How Stress Contributes to Urinary Retention
There are several ways in which stress can contribute to urinary retention. First, stress can lead to an overactive bladder, where the bladder muscles contract involuntarily, causing the urge to urinate more frequently. This can make it difficult for the bladder to empty completely, resulting in urinary retention.
Additionally, stress can lead to the development of unhealthy habits such as holding in urine for long periods of time, which can weaken the bladder muscles and further exacerbate urinary retention. Furthermore, stress can cause the muscles in the pelvic floor to become tense and tight, which can make it more difficult for the bladder to empty completely.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Stress-Induced Urinary Retention
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of stress-induced urinary retention in order to address the issue and seek appropriate treatment. Common symptoms include difficulty starting urination, weak or interrupted urine flow, an urgent need to urinate, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. In some cases, individuals may also experience pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
If you suspect that stress may be contributing to your urinary retention, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional who can help identify the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Managing Stress to Improve Bladder Function
One of the most effective ways to prevent and alleviate stress-induced urinary retention is to manage and reduce stress levels. There are numerous stress management techniques that can be implemented to help improve bladder function, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation.
In addition to stress management practices, it is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, all of which can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
Seeking Medical Help for Urinary Retention
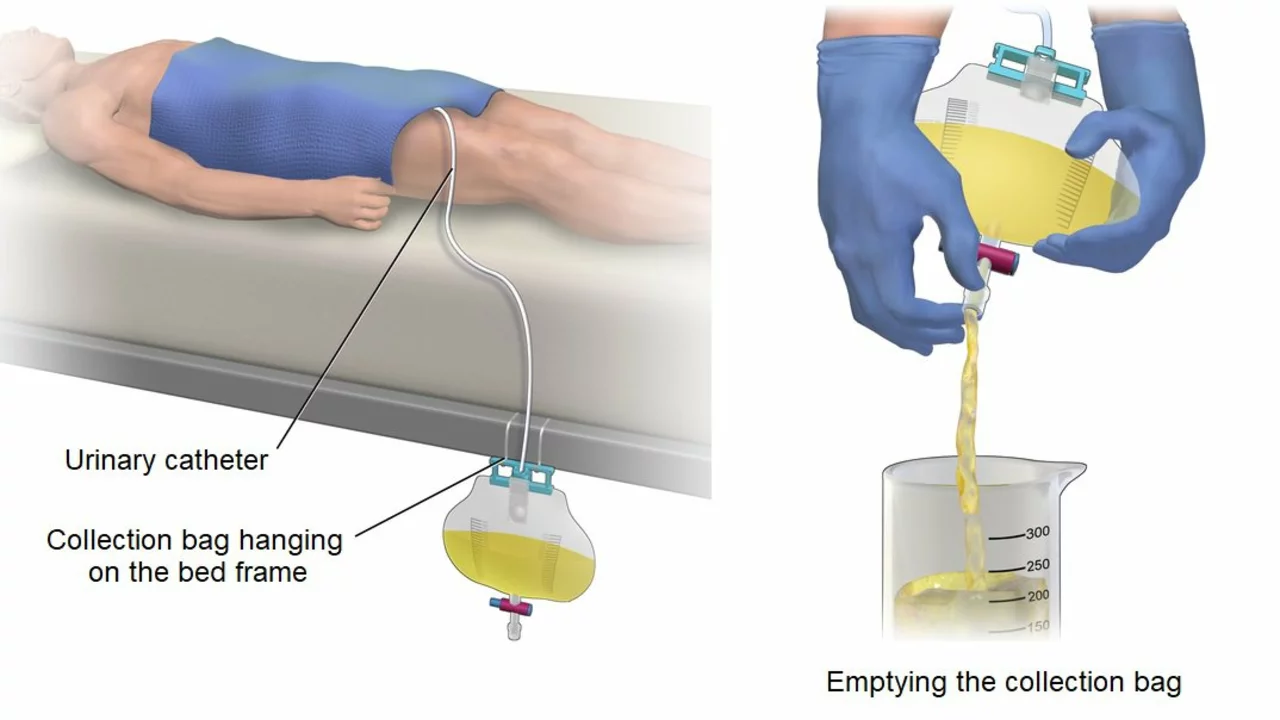
If you are experiencing urinary retention, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Depending on the underlying cause, treatment may include medications, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgical intervention.
It is crucial to address urinary retention early on, as untreated cases can lead to serious complications, such as urinary tract infections, kidney damage, and bladder damage.
Exploring Alternative Therapies for Urinary Retention
In addition to traditional medical treatments, there are also a variety of alternative therapies that may be helpful in addressing stress-induced urinary retention. Some options include acupuncture, biofeedback, and herbal remedies. However, it is important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional before beginning any new treatment, as not all alternative therapies may be appropriate for every individual.
Understanding the Connection Between Mental Health and Urinary Retention
It is essential to recognize the connection between mental health and urinary retention, as stress and anxiety can have a significant impact on bladder function. Addressing mental health concerns, such as anxiety and depression, through therapy and medication can be an important part of treating and managing urinary retention.
By taking a holistic approach to treatment, individuals can better understand the underlying causes of their urinary retention and work towards finding effective solutions to improve their overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: The Importance of Addressing Stress in Urinary Retention
In conclusion, stress plays a significant role in causing and exacerbating urinary retention. By recognizing the symptoms of stress-induced urinary retention and implementing stress management techniques, individuals can improve their bladder function and overall health. It is important to seek medical help for urinary retention and explore both traditional and alternative therapies in order to find the most effective treatment plan for each individual.
By understanding the connection between stress and urinary retention, we can work towards finding effective solutions that address the root cause of the issue and promote overall well-being.






Elizabeth Nisbet May 4, 2023
Hey folks, great info here! If you’re feeling the pressure, remember to breathe deep and give your pelvic floor a gentle stretch. Consistency with relaxation exercises can make a huge difference over time. Keep listening to your body and don’t hesitate to ask a professional for guidance. You’ve got this!
Sydney Tammarine May 4, 2023
Honestly, the mere mention of “stress” without deep philosophical context feels almost pedestrian 😒. One must consider the existential weight of modern anxieties, a topic far beyond the layperson's grasp. The article barely scratches the surface of the profound mind‑body dichotomy that scholars have debated for centuries. It’s a shame that such a nuanced subject is relegated to a simplistic health checklist. 🙄
josue rosa May 4, 2023
Stress-induced urinary retention represents a multifactorial pathophysiological process that intertwines autonomic dysregulation with somatic pelvic floor hypertonicity. The hypothalamic‑pituitary‑adrenal axis, when chronically activated, releases cortisol and catecholamines that modulate detrusor contractility through β‑adrenergic receptors. Concurrently, elevated sympathetic tone can inhibit parasympathetic efferents that ordinarily mediate bladder emptying, thereby fostering incomplete voiding cycles. Moreover, chronic stress precipitates maladaptive neuroplastic changes within the sacral spinal cord, altering afferent signaling from the bladder afferents. This neurogenic alteration contributes to heightened sensory thresholds and delayed micturition reflexes. In addition, stress often promotes behavioral patterns such as voluntary urine retention, which further attenuates bladder compliance. The resulting mechano‑stretch of the bladder wall can induce inflammatory cascades involving interleukin‑6 and tumor necrosis factor‑α, exacerbating detrusor overactivity. Research indicates that pelvic floor muscle hypertonicity, mediated by increased gamma‑aminobutyric acid (GABA) inhibition, creates a functional outflow obstruction. Clinicians should therefore assess both psychogenic and somatic contributors when evaluating patients with retention symptoms. Biofeedback and electromyographic studies can elucidate the degree of pelvic floor rigidity. Pharmacologic interventions targeting α‑adrenergic receptors may provide symptomatic relief, yet they must be balanced against systemic hemodynamic effects. Integrative approaches, such as cognitive‑behavioral therapy, aim to attenuate the central stress response and restore autonomic equilibrium. Additionally, mindfulness‑based stress reduction has demonstrated efficacy in reducing cortisol levels and improving bladder capacity. It is imperative to adopt a multimodal treatment algorithm that addresses hormonal, neural, and muscular components. Future investigations should focus on longitudinal outcomes of combined psychophysiologic therapies. Ultimately, a comprehensive strategy that mitigates chronic stress may prevent the progression from intermittent difficulty to chronic urinary retention.
Shawn Simms May 4, 2023
The article provides a concise overview of the interplay between psychosocial stressors and lower urinary tract function. It rightly emphasizes the necessity of a thorough clinical evaluation to differentiate neurogenic from obstructive etiologies. While the discussion of alternative therapies is appreciated, empirical evidence remains limited. Readers would benefit from references to randomized controlled trials supporting these modalities. Overall, the piece maintains a balanced perspective.
Geneva Angeles May 4, 2023
Wow, what an empowering read! It’s amazing how simply managing our daily stressors can translate into tangible improvements for bladder health. By incorporating mindfulness practices, gentle yoga, and regular aerobic exercise, we’re not just easing tension-we’re actively rewriting the script of our body’s response to pressure. Imagine waking up feeling light, with the confidence that your bladder will cooperate throughout the day. This positive feedback loop fuels motivation, encouraging us to stay consistent with our wellness routines. And let’s not forget the power of community support; sharing tips and successes with friends can amplify those benefits. Keep the momentum going, and remember that every small step builds a healthier future.
Scott Shubitz May 5, 2023
Okay, let’s cut the fluff-stress is a sneaky little beast that loves to hijack your bladder and leave you holding it like a protester in a frozen queue. It tightens up that pelvic floor like a drum skin ready to snap, and your poor detrusor just throws up its hands in surrender. If you’re fed up with playing hostage to anxiety, it’s time to give that stress the boot with some hardcore breathing drills and maybe a dash of that meditation hype. Don’t buy into every “miracle cure” out there, but do consider a solid biofeedback session to teach those muscles who’s boss. Trust me, the payoff is worth the sweat.
Soumen Bhowmic May 5, 2023
Hey team, I totally agree with the points made about stress management and bladder health. Combining gentle stretching with a balanced diet seems like a win‑win strategy. It’s also helpful to track fluid intake and bathroom habits to spot patterns early. If anyone has tried a specific relaxation app, feel free to share-it could help others streamline their routine. Let’s keep supporting each other on this journey!
Jenna Michel May 5, 2023
Absolutely! 😊! You nailed it-consistent breathing, pelvic floor awareness, and a dash of positivity can truly transform outcomes!!! Remember, it’s okay to stumble; the key is to get back up and keep moving forward-your body will thank you!!! Keep crushing those goals, and don’t forget to celebrate every tiny victory!!!
Abby Richards May 5, 2023
Nice take! 🙃
Lauren Taylor May 5, 2023
Thank you for highlighting the vivid challenges that stress can impose on our urinary systems. It’s important that we recognize how diverse cultural attitudes toward mental health influence the willingness to seek help. By fostering an inclusive environment where patients feel safe discussing anxiety, we can better address the physiological repercussions you described. Collaborative care models that integrate urologists, mental health professionals, and physiotherapists have shown promise in mitigating stress‑related retention. Let’s continue to share evidence‑based practices and ensure that no one feels alienated by the complexity of their symptoms. Together, we can dismantle barriers and empower individuals to take proactive steps toward holistic well‑being.
Vanessa Guimarães May 5, 2023
Oh, brilliant, because the solution to a physiological issue is obviously a grand conspiracy of “big pharma” and “mind control” agents, right? 🙄 In all seriousness, while inclusive language is nice, we still need concrete data, not just feel‑good rhetoric. Let’s focus on rigorous studies rather than speculative narratives. After all, the health of the bladder is not a political battleground. It’s time to separate hype from hard science.