The Rising Trend of E-Commerce
It's no secret that e-commerce has been on the rise over the past decade, and its impacts on urban congestion can no longer be ignored. With the increasing number of online shoppers and the convenience of having products delivered directly to our doorsteps, we need to consider the effects this trend has on our cities and their infrastructure. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which e-commerce is contributing to urban congestion and discuss potential solutions to mitigate these issues.
Surge in Delivery Vehicles
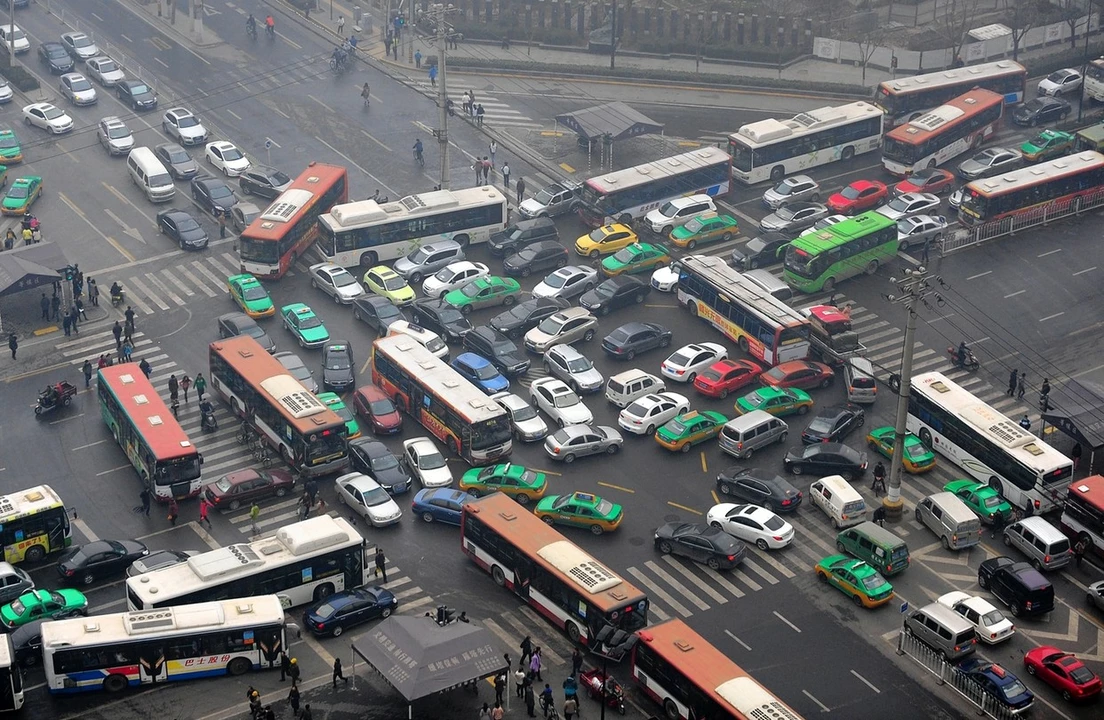
One of the most visible impacts of e-commerce on urban congestion is the significant increase in delivery vehicles on our roads. As online shopping continues to grow in popularity, so does the demand for fast and efficient delivery services. This has resulted in a surge of delivery trucks and vans navigating through already crowded streets, adding to the overall traffic and pollution levels in our cities.
Increased Demand for Warehousing and Distribution Centers
Another factor contributing to urban congestion is the increased demand for warehousing and distribution centers. E-commerce businesses require large, strategically located spaces to store and manage their inventory. These facilities are often situated close to urban centers, resulting in increased traffic and congestion as delivery vehicles travel to and from these locations.
On-Demand Delivery Services
On-demand delivery services, such as food delivery apps and courier services, have also played a significant role in exacerbating urban congestion. These services rely on a fleet of drivers who are constantly on the move, picking up orders and delivering them to customers. The convenience of these services has led to a rapid increase in their use, further contributing to traffic issues in urban areas.
Impacts on Public Transportation
The rise of e-commerce has also had indirect effects on public transportation. With more people opting to shop online and have their purchases delivered, fewer individuals are using public transit to travel to brick-and-mortar stores. This decline in ridership can lead to reduced funding for public transportation, resulting in lower quality services and potential cutbacks, thereby encouraging more people to use private vehicles and adding to urban congestion.
Last-Mile Delivery Challenges
Last-mile delivery - the final step of the delivery process - is one of the most significant contributors to urban congestion. As delivery vehicles navigate through dense city streets to reach their final destination, they often double-park, block traffic lanes, and contribute to overall gridlock. Additionally, the need for fast delivery times puts pressure on drivers to complete their routes quickly, potentially leading to unsafe driving practices.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of e-commerce and its contribution to urban congestion cannot be overlooked. The increased number of delivery vehicles on the road results in higher levels of air pollution, noise pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the energy consumption associated with warehousing and distribution centers contributes to an overall increase in the carbon footprint of e-commerce operations.
Strain on Infrastructure
Urban congestion caused by e-commerce also places a significant strain on city infrastructure. Traffic congestion can lead to increased wear and tear on roads and bridges, necessitating costly repairs and maintenance. Additionally, the increased demand for warehousing and distribution centers can lead to the development of valuable land that could otherwise be used for housing or other essential city services.
Potential Solutions to Mitigate Congestion
Addressing the issue of urban congestion caused by e-commerce requires a multifaceted approach. Some potential solutions include improving the efficiency of delivery routes, promoting the use of electric and low-emission vehicles, and implementing congestion pricing to discourage private vehicle use during peak hours. Additionally, investing in the improvement and expansion of public transportation infrastructure can help reduce the reliance on private vehicles and alleviate congestion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rapid growth of e-commerce has had significant impacts on urban congestion. As we continue to embrace the convenience of online shopping and on-demand delivery services, it is crucial that we consider the effects on our cities and work towards implementing solutions that will mitigate these issues. By addressing the challenges associated with e-commerce and urban congestion, we can help create more sustainable, livable cities for future generations.







Angie Wallace April 29, 2023
Think of delivery routes like a workout plan, steady and efficient.
Doris Montgomery May 6, 2023
The piece merely scratches the topic, offering generic observations rather than solid statistics. It mentions more vans on the road but fails to quantify the increase. A deeper dive into actual congestion metrics would have made the argument more compelling.
Nick Gulliver May 13, 2023
Our city streets are choking under a flood of delivery trucks, and it feels like outsiders are dumping their goods without regard for our commuters. The constant honking and double‑parking erode the quality of urban life we deserve. It's high time we prioritize local traffic over endless online orders.
Sadie Viner May 21, 2023
The proliferation of e‑commerce has undeniably reshaped urban logistics in a manner unprecedented in modern history. Delivery fleets now criss‑cross metropolitan arteries at a volume that rivals traditional freight operations. This surge places an additional burden on already strained road networks, accelerating wear and escalating maintenance costs. Moreover, the concentration of distribution hubs near city centers exacerbates peak‑hour congestion, as trucks queue for loading and dispatch. The phenomenon of last‑mile delivery introduces further complexity, with vehicles executing frequent stops that disrupt traffic flow. Pedestrians and cyclists also bear the brunt of erratic maneuvering, as drivers vie to meet tight service windows. From an environmental perspective, each supplementary vehicle contributes to elevated greenhouse gas emissions and localized air pollutants. Although e‑commerce promises efficiency, the externalities imposed upon urban ecosystems warrant rigorous mitigation strategies. Cities worldwide are experimenting with low‑emission zones, incentivizing electric delivery vans to curtail carbon output. Congestion pricing mechanisms offer a fiscal lever to discourage non‑essential trips during rush hours, thereby reclaiming road capacity for essential services. Consolidated delivery models, such as micro‑fulfilment centers embedded within residential districts, can shrink travel distances dramatically. Additionally, the adoption of smart routing algorithms leverages real‑time data to optimize paths, minimizing idle time and fuel consumption. Public policy must also address the fiscal shortfall faced by transit agencies as retail foot traffic wanes, ensuring continued investment in mass‑transit infrastructure. By harmonizing private logistics with public transportation planning, municipalities can foster a multimodal ecosystem that reduces reliance on single‑occupancy vehicles. In sum, a holistic approach-encompassing technological innovation, regulatory frameworks, and community engagement-is essential to prevent e‑commerce from undermining urban livability.
Kristen Moss May 28, 2023
Nice breakdown, but seriously, those massive warehouses popping up near downtown are a nightmare. They steal land that could house families, and the traffic they spawn is just the cherry on top of a messed‑up system. We gotta push back hard on that expansion.
Rachael Tanner June 5, 2023
Urban logistics resemble a tangled spider’s web, each strand pulling at the other. When e‑commerce adds new threads, the whole structure strains under pressure.
Debra Laurence-Perras June 12, 2023
You’ve captured the complexity beautifully; it’s a vivid picture of our streets. Let’s keep sharing ideas to untangle that web together.
dAISY foto June 20, 2023
Yo fam, the online shop wave is like a tidal surge hittin’ our city lanes-crazy ride, right? When you order that pizza at 2 am, a bike whips through traffic like a ninja. It’s wild how a click turns into a dash of wheels on the block. Gotta love the hustle, but also feels like the streets are trippin’ over each other.
Ian Howard June 27, 2023
Indeed, the surge in micro‑deliveries injects a pulsating rhythm into urban arteries, yet the resulting turbulence can erode the very fabric of roadway safety. Deploying dynamic lane allocation and real‑time monitoring could temper this chaos, channeling the energy into smoother flows.
Chelsea Wilmer July 4, 2023
One might argue that the digital marketplace is not merely a commercial conduit but a philosophical reshaping of space and time within the metropolis. As consumers, we outsource not only our purchases but also the very act of movement, surrendering our footsteps to algorithmic itineraries. This surrender subtly redefines our relationship with the urban environment, turning streets into data‑driven conveyor belts. The relentless cadence of delivery vans becomes a metronome marking the rhythm of modern life, echoing the ceaseless hum of progress. Yet, with each parcel delivered, we inch further from the tactile experience of communal marketplaces that once fostered social cohesion. The loss of these shared spaces may exacerbate social fragmentation, even as efficiency soars. Moreover, the carbon imprint of countless small shipments aggregates into a substantial environmental toll that is often obscured by the allure of convenience. Ultimately, the e‑commerce boom invites us to contemplate the balance between convenience and communal vitality.
David Stout July 12, 2023
You’ve laid out the philosophical stakes brilliantly, and now it’s time to translate that insight into action. Communities can rally for greener delivery options, lobby for stricter zoning, and champion shared pickup hubs. Let’s turn this awareness into a catalyst for positive change.
Pooja Arya July 19, 2023
In the grand tapestry of civilization, we stand at a crossroads where convenience battles conscience. The ceaseless flow of parcels threatens to erode the moral fabric of our neighborhoods, turning bustling avenues into sterile corridors of consumption. Yet, within this turmoil lies an opportunity for collective awakening, a chance to re‑imagine urban living beyond the relentless ping of notifications.
Sam Franza July 27, 2023
We need balanced policies that protect both residents and businesses while keeping streets safe.
Raja Asif August 3, 2023
Exactly, but the solution is to enforce strict limits on foreign delivery firms flooding our roads, safeguarding national traffic flow.